BigData: Hbase et architecture de projet avec JBoss EAP 6.1
Le but du jeu de cet exemple est de créer un projet RESTfull qui insère des données dans une base HBase. Ces services web seront exposés sur un serveur JEEJava Entreprise Edition JBoss EAP 6.1.
Installer HBase
Premièrement, il faut installer une base Hbase sur un serveur linux. Il est possible de l’installer sur un serveur windows, mais ceci est plus compliqué à réaliser. Nous ne traiterons pas de l’installation de HBase dans ce post car il existe de nombreux tutoriels très bien faits sur le net.
Architecturer son projet
La première question concernant le projet est de savoir comment architecturer le projet JEE. Sans prétendre être la meilleure solution, voici celle que nous avons mis en place dans le projet:
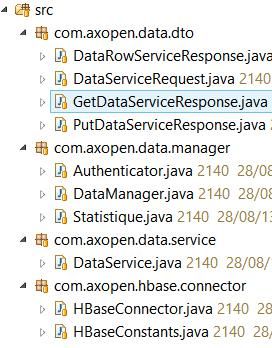
- Le premier package correspond aux DTO qui seront véhiculés par les services REST. En POST.
- Les managers, et en particulier DataManager, correspondent à la classe qui a la responsabilité de sauvegarder les données dans la base HBase
- Les services sont les services JSON qui réceptionnent les données en POST ou en GET.
- Enfin, la partie connector permet de gérer la connexion avec la base de données.
La connexion à la base de données HBase
Ce code permet de bien gérer la connexion à la base de données HBase depuis votre application et en particulier depuis vos managers.
package com.axopen.hbase.connector;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HColumnDescriptor;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HTableDescriptor;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.MasterNotRunningException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ZooKeeperConnectionException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HBaseAdmin;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTableInterface;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTablePool;
public class HBaseConnector {
private static HBaseConnector instance;
private static HTablePool hTablePool;
private static Configuration mConfiguration;
/**
* Private Constructor
*/
private HBaseConnector() {
try {
// CONFIGURATION
Configuration lConfiguration = new Configuration();
try {
HBaseAdmin.checkHBaseAvailable(lConfiguration);
} catch (MasterNotRunningException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (ZooKeeperConnectionException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
// PERMET DE VERIFIER LA CONFIGURATION ET L’ACCES AU SERVEUR
mConfiguration = HBaseConfiguration.create(lConfiguration);
// CREATION D’UN POOL DE TABLE
hTablePool = new HTablePool(lConfiguration,
HBaseConstants.HTABLE_POOL_SIZE);
// CREE LA DATABASE SI NON EXISTANTE
initDatabase();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Creates the tables and table columns in the database.
*
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void initDatabase() throws IOException {
HBaseAdmin admin = new HBaseAdmin(mConfiguration);
HTableDescriptor[] blogs = admin.listTables(HBaseConstants.STATSTABLE);
if (blogs.length == 0) {
HTableDescriptor blogstable = new HTableDescriptor(
HBaseConstants.STATSTABLE);
admin.createTable(blogstable);
// Cannot edit a stucture on an active table.
admin.disableTable(HBaseConstants.STATSTABLE);
// META DATA
HColumnDescriptor metadesc = new HColumnDescriptor(
HBaseConstants.META);
admin.addColumn(HBaseConstants.STATSTABLE, metadesc);
// DATA
HColumnDescriptor datadesc = new HColumnDescriptor(
HBaseConstants.DATA);
admin.addColumn(HBaseConstants.STATSTABLE, datadesc);
// For readin, it needs to be re-enabled.
admin.enableTable(HBaseConstants.STATSTABLE);
}
admin.close();
}
/**
* @return The HbaseTableManager instance
*/
public static HBaseConnector getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new HBaseConnector();
}
return instance;
}
/**
* Method used to retrieve a HTable instance.
*
* @param tableName
* The table name
* @return The HTableInterface instance
* @throws IOException
*/
public synchronized HTableInterface getHTable(String tableName)
throws IOException {
return hTablePool.getTable(tableName);
}
}
Utilisation de votre base de données (Hbase)
Enfin pour utiliser votre base de données, il suffit juste d’utiliser votre Singleton nouvellement créé.
HTableInterface table = HBaseConnector.getInstance().getHTable(
HBaseConstants.STATSTABLE);
Nos podcasts en lien
Pour aller plus loin
Les nouvelles technologies
Découvrez la planche #71 !
Growing up
Découvrez la planche #48 !
Tuto : utiliser Cypress pour ses tests End-to-End
L’écriture de tests automatisés est souvent perçue par les développeurs comme une tâche ingrate et chronophage. Certes, les tests n’apportent rien de plus au rendu visuel du projet web, mais ils sont pourtant essentiels pour assurer la fiabilité d’une application sur le long-terme. Et si on vous disait qu’il existe un outil capable de rendre cette tâche bien moins fastidieuse ? Voici Cypress !